What are the key parameters for a successful Food Delivery Drone?How to determine the minimum delivery range and ideal payload weight? What is the ideal delivery mechanism? How can reduced delivery time improve competitiveness and higher payloads expand the potential customer base?
Drones: From Industrial use to Food Delivery
Industrial use
Initially drones have seen early adoption in Surveillance and Security, Mapping and Inspection and Detection industries because of the remote locations they have been easier to deploy there.
Suburban life convenience
Now drones do not only enhance the above industrial and commercial processes, delivery drones can also add a lot of value to logistical supply chains. Of late there has been a growing interest in the benefits that delivery drones can bring to commerce in general and the daily routines of people in particular, where the promise of having food delivered to you wherever you are, via a drone, is gaining traction.
Home Delivery Market
Growth
Online Food Delivery (FD) platforms have taken off and represent a $350bn market today as these platforms are enticing consumers away from cooking or eating out to eating in the comfort of their own homes, or where ever they happen to be at a given moment. In the major markets of China, US, India, UK and Brazil, annual growth rates range from 5% to about 10% per annum. Worldwide online FD has become well accepted are clearly here to stay with many platforms having become household names.
Business models
Online FD platforms connect restaurants with consumers providing choices, facilitates orders and payments and arranging delivery through Delivery people. This achieved through a variety of business models and combinations of restaurants, platform providers and riders.
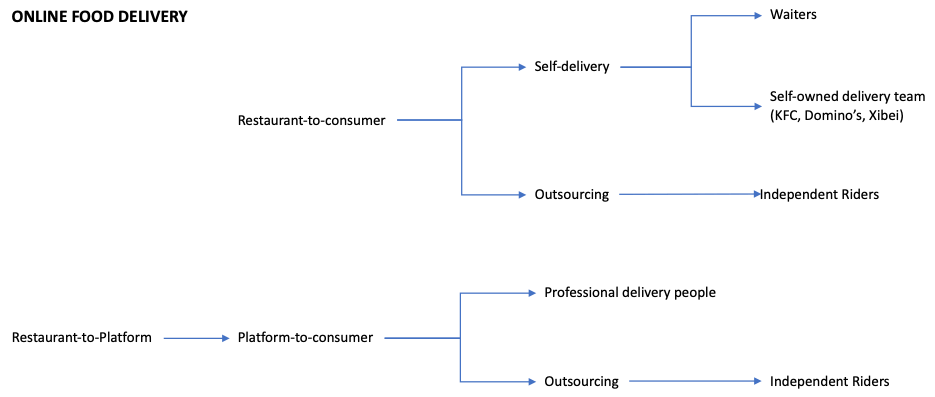
Socio-economic impact
- While 100,000’s job opportunities have been created, job satisfaction is low, and restaurants had to evolve new business models
- Online FD has contributed to a convenient urban life, it also has had an impact on public traffic and provided a crucial service during COVID-19.
- It has also contributed to increased public and food waste as well as an increased carbon footprint.
Current state of online Food Delivery
• A cursory review of online FD websites reflect low online satisfaction ratings with 60% OF ORDERS TAKING 28 MINUTES TO DELIVER.
• Riders work in poor conditions, earning about 5 EUR per delivery, making 2.2 deliveries per hour and in unsafe condition with 180 recorded injured and 70 dead in the UK.
The Economics of online Food Delivery
Average cost of online food order
A review of online FD platforms show that about 66% of food ordered totalled up to about $30 per order placed, with the range typically being between $15 and $50. Of this about 30 – 40% about is for delivery costs (which includes an extra markup by restaurants that some of them apply to the base price of food sold via online FD platforms and delivered to the customers place). Salaries form the largest portion of food delivery costs.
Different prices were listed on online FD platforms like Postmates, Uber Eats, DoorDash and Grubhub. For an average family meal of $40 the following breakdown applied:

Food delivery radius
- An accepted rule of thumb is that AT LEAST 10,000 HOUSEHOLDS SHOULD BE IN A DELIVERY RADIUS to justify a road (motorcycle/car) based FD service economically.
- A delivery radius may vary significantly from in a city, (1.6km or 3.2km radius) to a suburban area, (16–28 kms) for the same gas and delivery time.
- Generally a radius of 5km – 8km for a motorcycle or car would suffice.
- Domino’s Pizza delivers in a 17 min radius with a 30 min delivery promise.
- Typically 150-200 grams for per cooked evening meal

Food delivery timeline
ASSUMING 30–40 MINUTES TOTAL ORDER TIME, evenly distributed between preparation and delivery:
• 50% time will be taken to prepare, pack and dispatch the food 15min
• 50% for transit, finding address and delivering it. 15min
• Plus a buffer for traffic conditions and other unexpected events. 10min
Delivery drone
Food delivery by drones
One of the major challenges with end consumer oriented drone delivery, like food delivery is where and how to deliver. After navigating suburban airspace the drone (or drone pilot) has to find the exact location, land safely and deliver its consignment safely. Interacting with big food delivery drones is scary, and risky, for the untrained end consumer. This is emphasised by the fact that generally drone pilots are trained to keep bystanders at least 30m away from an armed drone (multi-copter) on the ground.
Dealing with above challenges the drone industry have come up with a few practical solutions. One of them is to deliver to a predefined, or pre-identified Drop Off point. Some of the solutions still require landing and an end consumer interacting with a drone that is ‘armed’ and still ready to take-off.

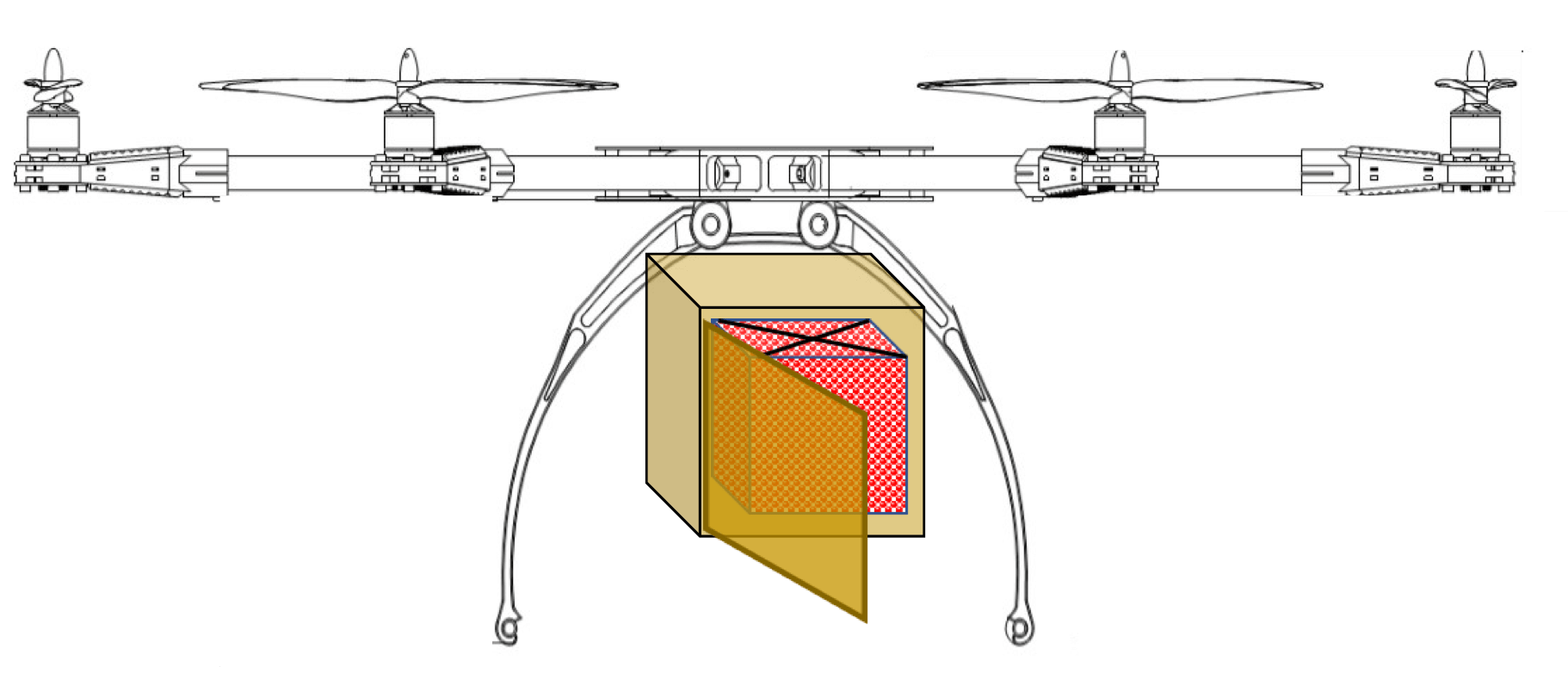
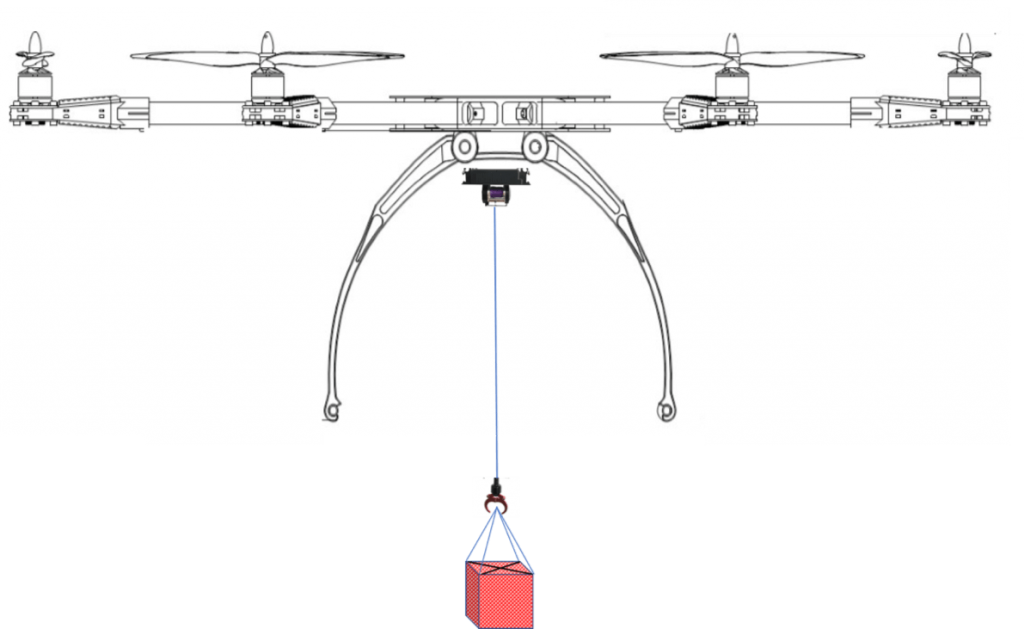
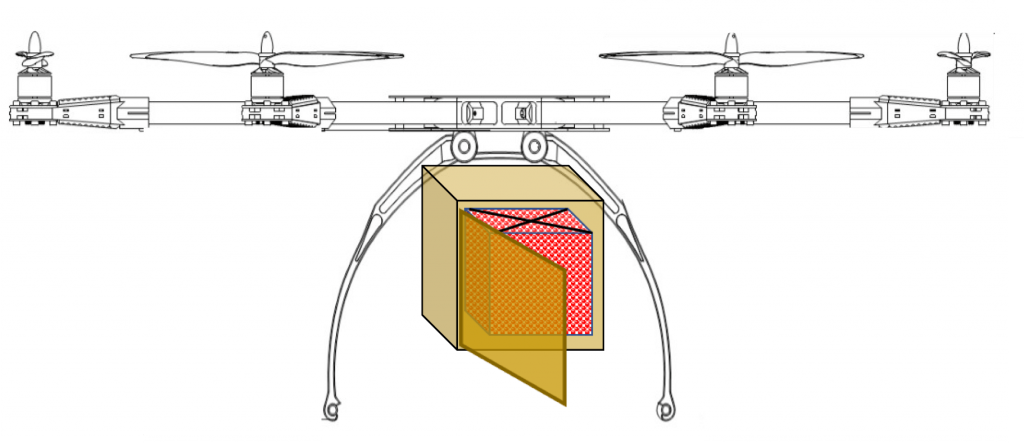
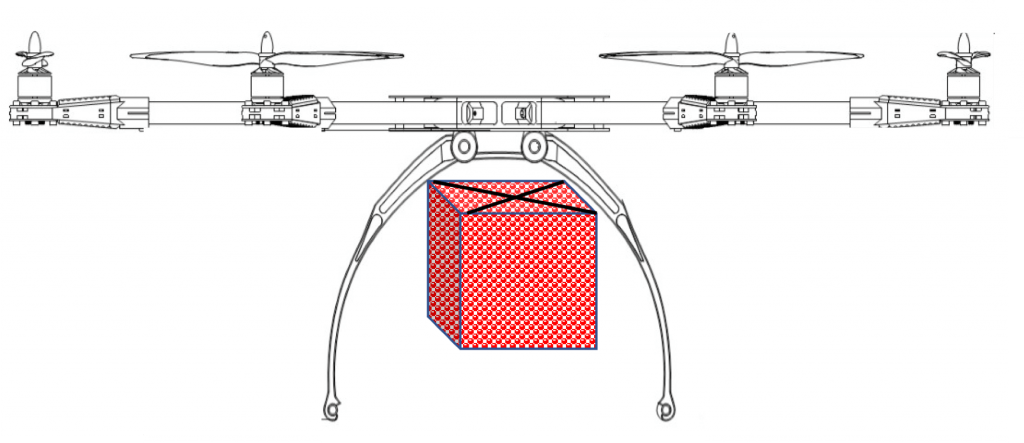
Drone Delivery mechanisms
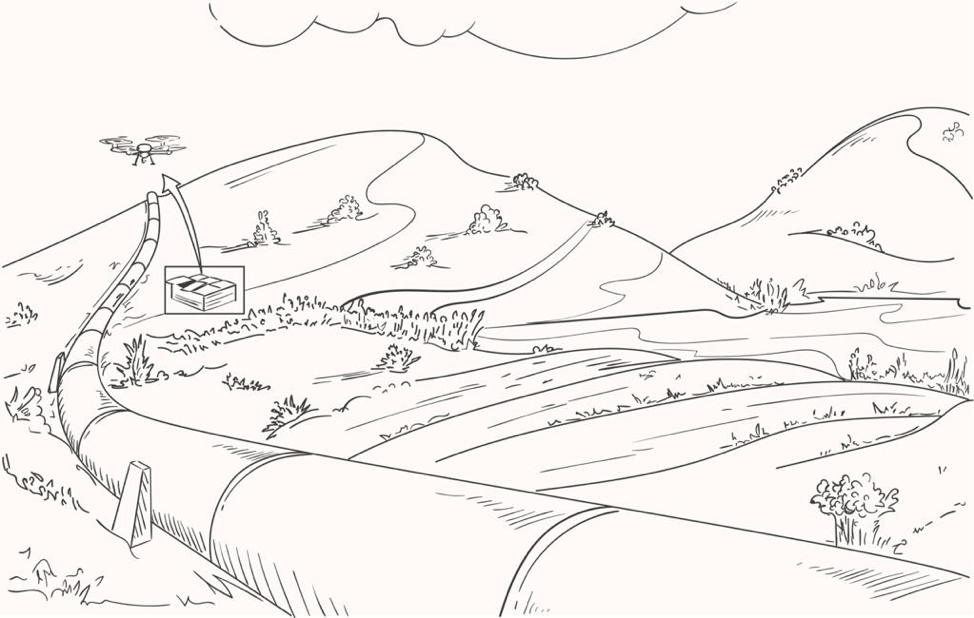
Another solution is lowering the consignment via a Tether and a Winch from a safe distance and delivering the food order via a quick release Claw and a disposable food carton.
[Delivering in built-up areas often often means drones are being flown in a 3D environment that is GPS-denied and with lots of EMI which can be very difficult to overcome. Being able to use DAA (Detect and Avoid) as well as an accurate digitised replica of the environment can be very useful to overcome these obstacles. Read how INSPECTION DRONES with full AUTONOMY and AI can assist.]
Noise level
An additional benefit of lowering a delivery, from say about 30m height is that it reduces the level of the drone. The noise level of some off the shelf consumer drones are very close the unacceptable noise level of 85 dBA. See drone noise levels.
At 30m above ground the drone’s noise level is likely to drop to what would amount to ambient noise levels in a suburb during the day of about 55dBA.
With a few variations the following drone food delivery mechanisms are the most popular ones:
Along with food delivery features, safety is a critical factor in urban and suburban drone deliveries, these drones also need to have advanced Detect and Avoid and Redundancy features to ensure the likelihood of failures has been reduced to nearly zero.
Currently an Irish drone manufacturer has been trailing an online FD drone solution with:
- a maximum carry weight of 2 to 4 kilograms
- in a 2km delivery radius,
- promising delivery within 3 minutes,
- has now been running for some weeks,
- claiming that just one of their drones are making between 20 and 50 deliveries a day
- at a cost of $3 to $5 per delivery.
An interesting study by ARK Investment provides a useful illustration of likely ‘last mile‘ delivery options and costs compared to Amazon Drones:
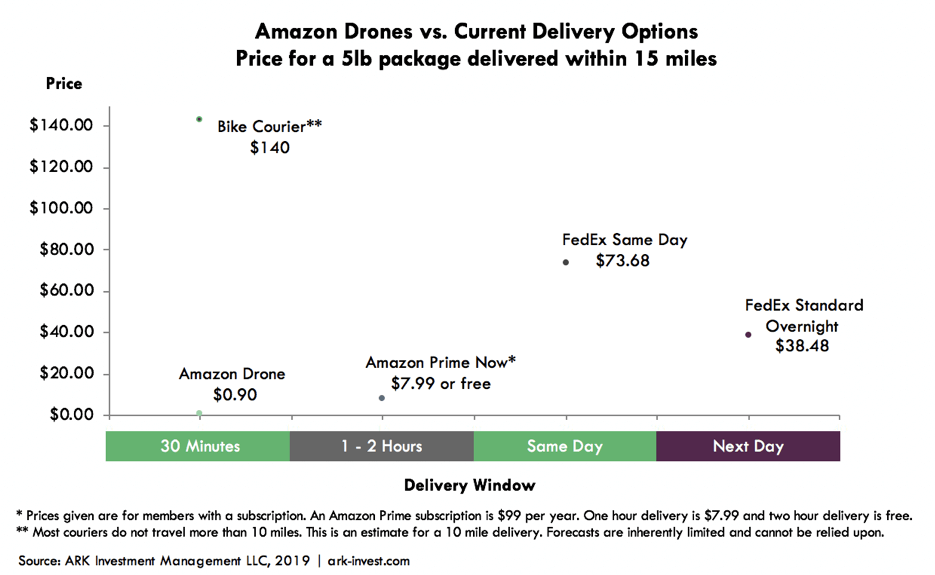
In Singapore, FoodPanda is trialling food delivery with drones over distances of up to 3km, using Singapore Technologies (ST) Engineering’s drone network system
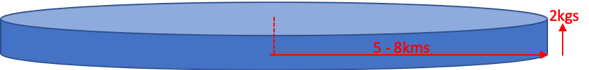
Typical drone payload
- a 2kg payload:
- translates to about 2 x Chinese takeaways or,
- 7 burgers & fries
- allows for a broader audience that includes not only singles, or couples, but also family meals,
- the larger payloads are also more profitable on a fixed delivery fee.
Drone delivery time
Drones can reduce delivery time of about 15 minutes to about 3 minutes.
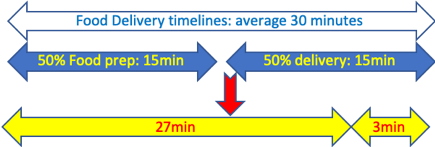
This benefit can be used in a variety of different ways.
Advantages of reducing food delivery time
- 1. Improves service delivery and increases customer satisfaction.
- In a standard delivery area radius of about 10kms, pickup-to-delivery times can be reduces from about 15 minutes to less than 5 minutes, or total order-to-delivery time from 30 minutes to less than 20 minutes.
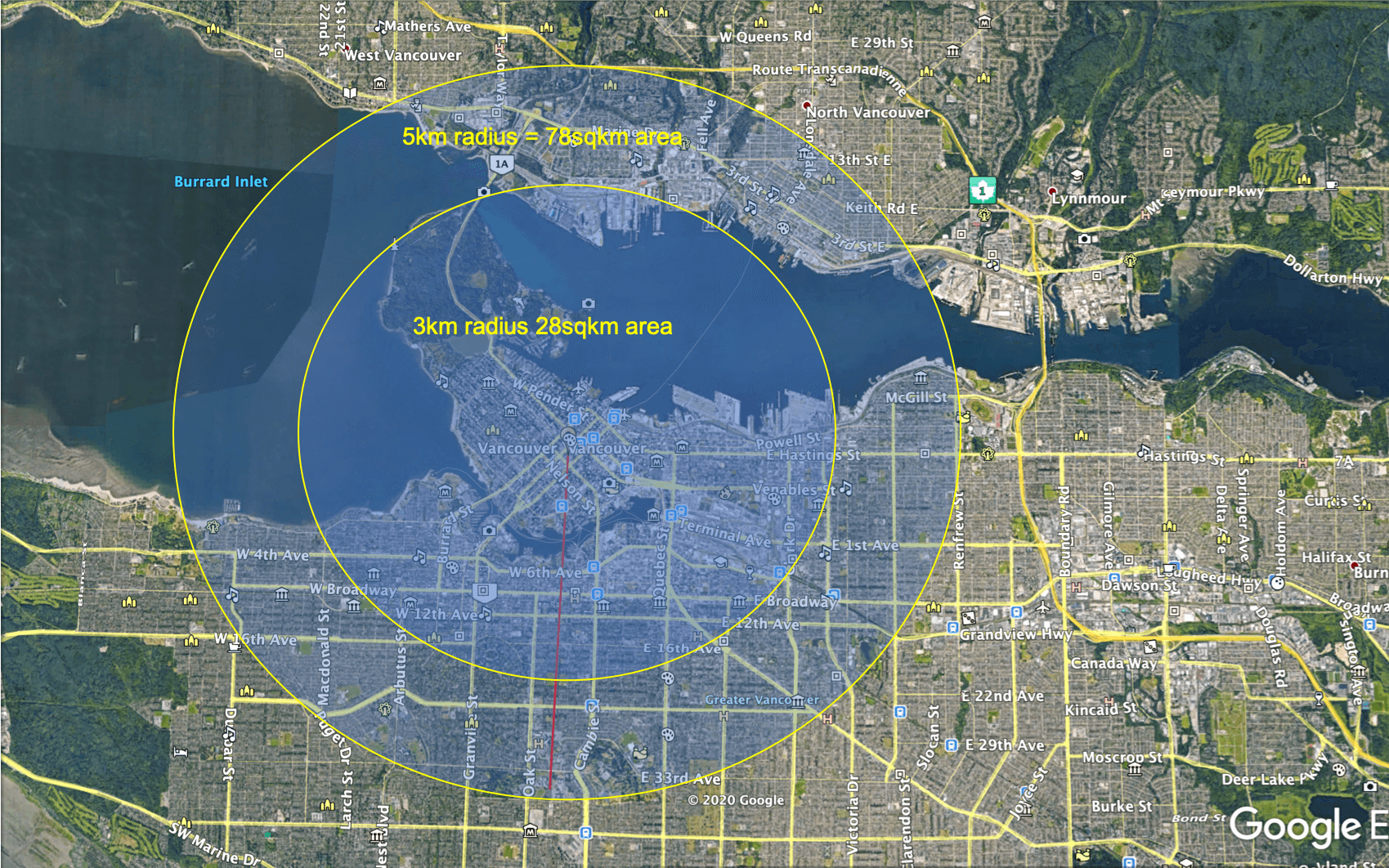
- 2. It can also increase delivery radius, making it possible to include more households per delivery area
a. In suburban areas the ratio is 500 households per km2- the following graphics shows how much more delivery area (6.4 x more) ) can gained by adopting drone technologies


- 3. It can also increase food preparation time by up to 80% enabling a wider variety of choices
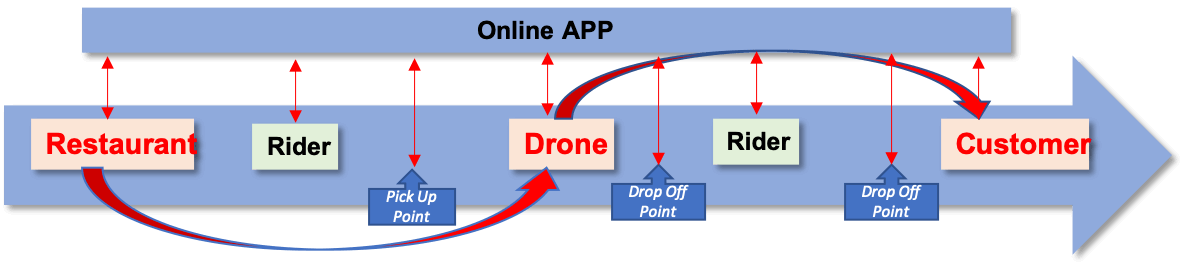
Drone-based food delivery processes.
Drone-based food delivery processes can use and combined a number of value chain elements (see Uber Eats example further down). Generally the key elements for drone based food delivery would be from the Restaurant, via Drone to the Customer. The process interacts and updates the online food ordering APP at various point during the workflow.
UBER Eats Drone
- Uber Eats have designed a solution, using Uber’s Elevate Cloud Systems, for delivery food via drones.
- The Uber Eat has designed a unique drone with VTOL features, It will be able to carry meals for up to 2 adults, travel a maximum of eight minutes with a total flight range is 26 kms, with a round-trip delivery range of 18kms.
- Drones are only used for a portion of the delivery. Once a customer orders food, the restaurant will prepare the meal and then load it onto a drone. That drone will then take off, fly and land at a pre-determined drop-off location.
- Uber’s Elevate Cloud Systems will track and guide the drone, as well as notify an Eats delivery driver when and where to pick up their food.
- Eventually Uber envisions landing the drones on top of parked Uber vehicles located near the delivery locations.
- From there, the Eats delivery driver will complete the last mile to hand-deliver the food to the customer.
The future for food delivery drones
It has been reported that food delivery services in the United Arab Emirates, are set to explode, especially for delivering food to areas where it’s not possible to drive. Other areas who are likely to deploy the early applications will be the US, Japan, South Korea, China, Australia, Singapore and Dubai, among others.
In these early stages of the economic feasibility food delivery drone projects are enhanced by targeting suburban areas, or regional towns, where aerial obstacles (such as high rise buildings) are minimal, but road access is more obstructed with obstacles such as:
- geological layout such a regional town, or city, built around a water mass, like a lake or river mouth, or mountains, etc
- traffic congestion,
- or climatic conditions like excessive heat.
These conditions also make it easier to demonstrate the economic viability of the food delivery drone projects.
The powerful, high endurance TETHERED FOOD DELIVERY DRONE platform from Airborne Drones is able to:
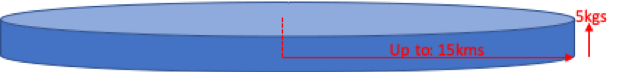
Maximize its payload (5kg).
Maximise delivery radiuses (using the full 15 minutes each way).
Using a simplified and low risk drone delivery method (tethered).
Perform multiple journeys on a single battery charge (high endurance).

Read more more about The Secrets to Building an Extra Long Range Quadcopter for real-world working applications here..
Read more about drones in Transport and Delivery here..